Hornwort
Hornwort
Common name: Hornwort;
Botanical name: Ceratophyllum demersum
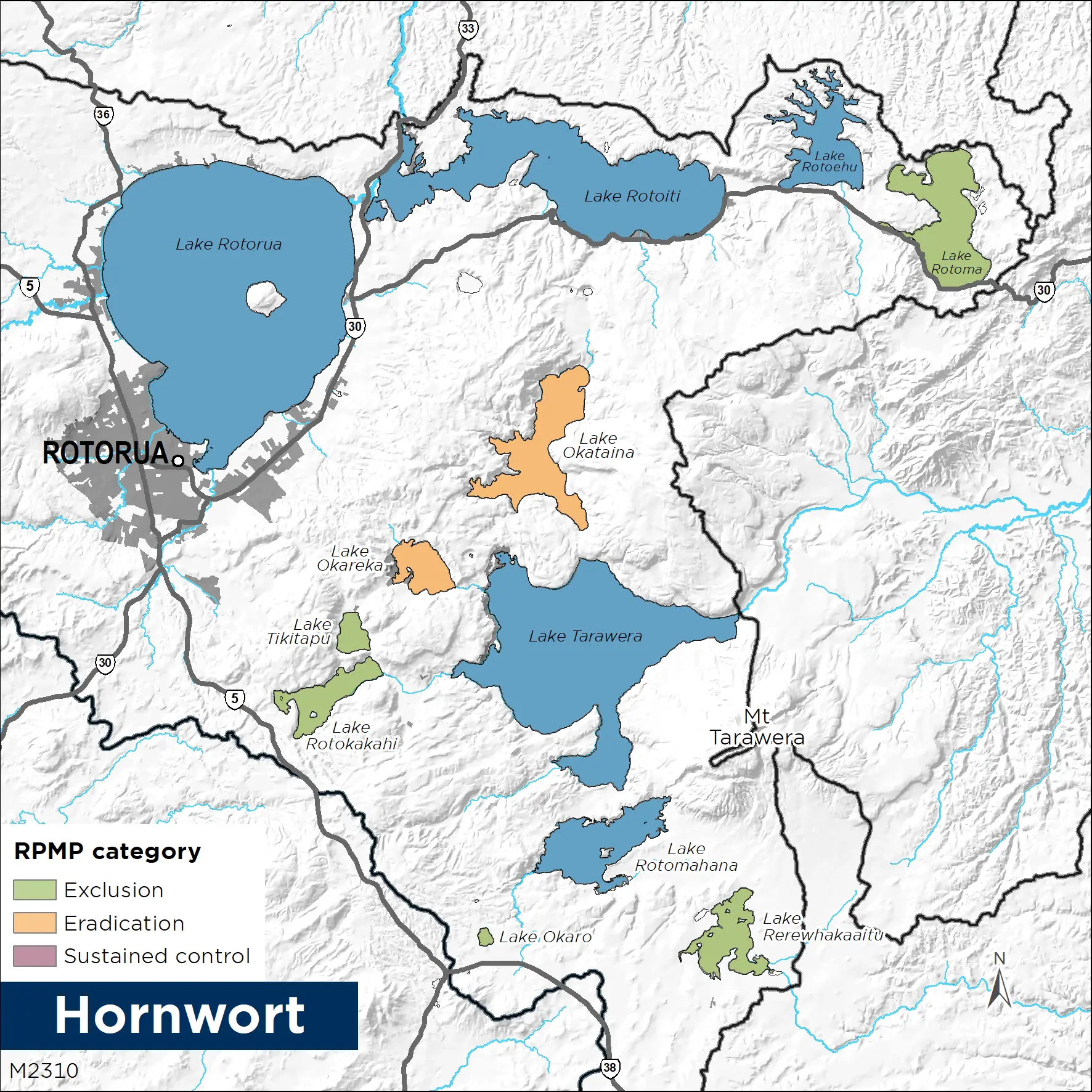
Management programme: Exclusion, Eradication, Progressive Containment
Hornwort is currently considered New Zealand’s worst submerged weed. Also known as coon tail; the tip of the plant is thick and looks similar to the tip of a racoon's tail. The free floating mats of hornwort have been known to have blocked hydro-electric dams in the past.
Why is it a pest?
- Grows up to 10m - much taller than other weed species.
- It can survive as a free-floating mat, absorbing all the nutrients it needs from the surrounding waters.
- Free floating mats of hornwort can grow to such large sizes that they completely shade out entire areas of lakes, inhibiting growth of native flora and fauna. Shallow lakes such as Lake Rotoehu are prime candidates for such exponential growth.
Where is it found?
- It is found in lakes, ponds, marshes, and slow flowing streams.
- Hornwort does not set seed in New Zealand, but reproduces from broken-off fragments that are easily moved to new sites via water movement and strong winds. Fragments also hitch rides on boats, trailers, nets and fishing gear.
- As at 2020, present in lakes Rotorua, Tarawera, Rotoiti, Ōkataina, Rotoehu, Ōkāreka and Rotomahana.
What does it look like?
- Hornwort is a submerged freshwater perennial aquatic plant that may occur as stems attached to the sediment or as a floating mat or drifting fragments.
- It has a very delicate appearance as the stems are thin and break easily through wave action.
- Whorled branched, narrow leaves, rough to the touch and densely crowded at the tip and sparse at the base.
- Narrow, bright green leaves 4cm long and finely divided.
- It does not have roots but may be anchored to the sediment by the base of its stems.
- The flowers are tiny (2mm long) in the leaf bases. Flowers are present November to March and are a white, pink, or greenish colour.
What are the rules?
Exclusion
Exclusion pests are not known to be present or established in the Bay of Plenty region. The Bay of Plenty Regional Council is responsible for managing new incursions into the region. Action may be required from landowners or occupiers to support a control operation.
Eradication
Eradication pests are present in the region but are limited in their size or extent of infestation. The eradication of these organisms is a feasible and cost-effective solution. The Bay of Plenty Regional Council is responsible for their control or eradication from the region. Action may be required from landowners or occupiers to support a control operation.
Progressive Containment
Progressive Containment species are pests which the Council aims to prevent from spreading, reduce the distribution, or eradicate within parts of the region over time. Landowners or occupiers are responsible for the control of Progressive Containment species on their property. Council may enforce the control of these pest species.
How do you get rid of it?
We are trying to prevent hornwort from getting into our waterways which have not been infested. If you are travelling with equipment or machinery between waterways please ensure that you check, clean, and dry.
If you would like advice on how to control hornwort please contact the Bay of Plenty Regional Council.
Images