Landslide
A landslide is defined as a mass movement of rock, soil and vegetation down a slope.
Landslides occur when the slope strength is overwhelmed by stresses imposed on it. These stresses can be sudden such as an earthquake or a severe weather event, or they can build up over time with the slope gradually weakening until what might seem a relatively insignificant event causes it to fail.
Slope failure
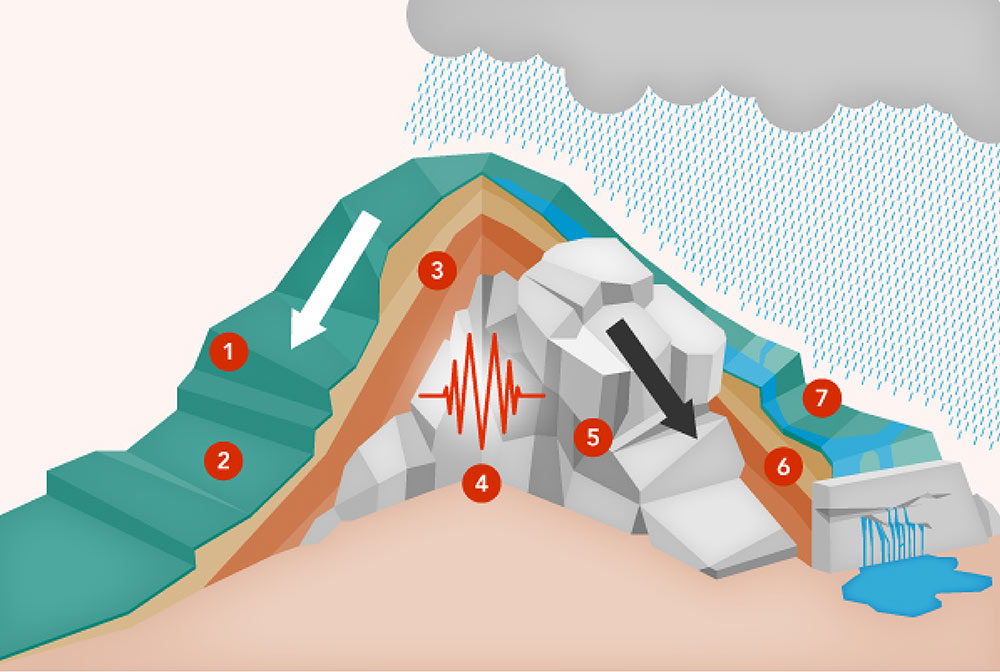
 The steeper the slope, the more unstable it will be.
The steeper the slope, the more unstable it will be.
 Plant roots hold the soil in place and the vegetation cover makes the soil surface more resistant to erosion.
Plant roots hold the soil in place and the vegetation cover makes the soil surface more resistant to erosion.
 Lack of frictional resistance between surfaces that separate one layer of rock from another can cause slop instability.
Lack of frictional resistance between surfaces that separate one layer of rock from another can cause slop instability.
 Earthquakes, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, the passage of heavy trucks, blasting and other sudden shocks may trigger the rapid movement of soil in slopes.
Earthquakes, hurricanes, volcanic eruptions, the passage of heavy trucks, blasting and other sudden shocks may trigger the rapid movement of soil in slopes.
 Cracks in the slope surface, or in the rock layers underneath, are vulnerable to disturbance or degradation.
Cracks in the slope surface, or in the rock layers underneath, are vulnerable to disturbance or degradation.
 Different types of soil are more erosion prone than others.
Different types of soil are more erosion prone than others.
 Excessive water and inadequate drainage: when heavy rain has saturated the soi, the earth becomes a lot heavier and prone to movement.
Excessive water and inadequate drainage: when heavy rain has saturated the soi, the earth becomes a lot heavier and prone to movement.
Landslides in New Zealand
Compared to many other countries, New Zealand has a high number of landslides because:
- Rocks are often weakened by geological folding and faulting
- There are frequent earthquakes
- Much of the land is hill country, formed by rivers cutting into soft clay rocks
- Many soft and easily erosion prone slopes have been cleared of vegetation as a result of agriculture
- Slopes can be unstable as a result of weak layers of volcanic ash and other fine windblown sediments.
- Rainfall can be high
What does this mean for the Bay of Plenty region?
Bay of Plenty Regional Council has initiated a region wide study to map landslide susceptibility for both seismic and extreme rainfall scenarios, particularly focusing on these urban areas:
- Waihī Beach
- Katikati
- Te Puna
- Paengaroa
- Te Puke
- Maketū
- Kawerau
- Rotorua
- Ōpōtiki
This information will be used for natural hazards planning and to identify areas where further assessment will be required for development. Completed mapping will be available to view in due course.
Where can I view these maps?
The Bay of Plenty regional landslide susceptibility maps will be available in due course on our mapping platform, BayHazards.
What do I do in a landslide?
For information on what to do in the event of a landslide, visit the Bay of Plenty Civil Defence website.
